Snow Hill station was opened by the London Chatham & Dover Railway on 1 August 1874 on the existing City Line between Ludgate Hill and Farringdon Street. It was renamed Holborn Viaduct Low Level 1.5.1912. The main entrance was on the north side of the viaduct consisting of a four storey building with a single storey above viaduct level. The booking hall was at basement level sandwiched between the road level and the trains below. A separate entrance was provided on Snow Hill from where a footpath led up to the east side of the station building. A covered way and a flight of steps linked the Low Level and High Level Stations.
The station was never well used and a census taken in 1911 showed there were fewer arrivals than at any other city station.
After the station had closed, trains were occasionally diverted by error into the Low Level platforms and access was initially maintained from the High Level station. The station entrance from Holborn Viaduct had become a tobacconist’s shop by 1926 and the basement level was then in use as a warehouse. By 1938, the Snow Hill entrance had been utilised to build a single storey cafe.
The 1940-1941 blitz flattened most of the block east of the railway including the four storey station building leaving just part of the station’s basement floor level, with a brick wall supported by the girders over the railway. These remains were removed completely around 1955, in preparation for roofing over the site prior to the building of a new office block over the site in the early 1960’s.
When the Greater London Council proposed to reopen the City Line in 1984 the proposal included a new Snow Hill station with a single island platform, to be sited between the running lines at this point, somewhat north of the original station site
BRIEF HISTORY OF THE LCDR’s ‘CITY LINE’
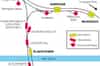
The Metropolitan Extensions Act of 1860 gave the London Chatham & Dover Railway access to the City, authorizing a 4.5 mile line from Herne Hill across the river to join the Metropolitan Railway at Farringdon Street.
The ‘City Line’ was far more than the Chatham could cope with financially, but the possibilities for through traffic were vast. To the north the G N R and the Midland could be reached and to the south were the L B S C R and L S W R at Clapham Junction from where the G W R and L N W R could be reached via the West London Line. All these companies were approached to partake financially and all eventually profited from the scheme gaining the right to work trains to their own goods and coal depots in South London.
The line from Herne Hill to the Elephant and Castle was opened on 6 October 1862 and on to Blackfriars Bridge on 1 June 1864. Intermediate stations were initially provided at Camberwell, Walworth Road and Borough Road and later at Loughborough Junction.
The Thames was eventually bridged and by 21 December 1864 a temporary station at Ludgate Hill was in use, a permanent station being opened on 1st June 1865. It had two narrow island platforms but the station was rebuilt in 1910 with a single broader island platform.
On 1st January 1866, L C D R passenger trains began running into the Metropolitan’s Farringdon Street station and the connection was soon carrying a wide variety of passenger and freight services. Then, by an Act of 13 July 1871, the Chatham became committed to yet another project. A nominally independent Holborn Viaduct Station Company (for the bankrupt Chatham was not allowed to raise capital) was authorized to build a 292 yard branch from the Ludgate - Farringdon line to a new terminus, complete with hotel, fronting on the new thoroughfare of Holborn Viaduct. It was opened on 2nd March 1874.
On 1st August 1874 a low-level station, Snow Hill (‘Holborn Viaduct Low Level’ from 1912), was opened at the foot of the 1 in 39 incline.
Finally, on 10th May 1886 a parallel bridge across the Thames was opened with, at the northern end, yet another new station, St. Paul’s, the original Blackfriars Bridge being closed. St. Paul’s was renamed Blackfriars on 1st February 1937. The existing layout was completed when the South Eastern Railway opened the Union Street spur on 1st June 1878 creating a through route into Charing Cross.
The difficulties of inter-terminal transfer through the congested streets of mid-Victorian London assured considerable transfer traffic. All L C D R mainline trains, including continental ones, carried a City portion attached or detached at Herne Hill. Eventually however the development of the underground network led to the withdrawal of the through services and the demise in the importance of Holborn and Blackfriars with a dramatic reduction in off peak services. Holborn retained very heavy parcels traffic, including continental and three of its six platforms, too short for electric trains were utilised.
The first casualty on the line was Borough Road which closed on 1st April 1907 due to competition from the Northern Line. As an economy measure during WW1 through services from south of the Thames to Moorgate via the Smithfield Curve (opened 1.9.1871) were withdrawn on 1st April 1916 with Camberwell and Walworth Road stations closing two days later. Holborn Viaduct Low Level closed on 1st June 1916 and with it through passenger traffic on the City Line ceased.
Less than 700 yards separated Holborn Viaduct from Blackfriars. Ludgate Hill thus became increasingly redundant, especially after the through trains stopped. The intensive Ludgate Hill - Victoria services were withdrawn during the First World War. The Wimbledon trains were the last to call and with their electrification it was closed on 3 March 1929.
In 1902, 19.2 million passengers used Holborn, Ludgate and St. Paul’s. Use declined with the loss of the cross London traffic until electrification. The growth of L.C.C. estates in S E London and Kent increased traffic but this was not maintained and in 1960 they were back to the 1902 level with 88% of the traffic arriving or departing during the rush hour. The ‘City Line’ was still a vital north-south freight link with some 90 trains a day in 1962, but all regular freight and parcels services were withdrawn in 1969. Although disused for many years the Snow Hill tunnel was finally abandoned in 1971 and the track was lifted.
The Snow Hill tunnel was reopened in 1988 as part of the new Thameslink network which came into service in May 1990, initially as part of British Rail but private since March 1997. To coincide with the opening of Thameslink, Holborn Viaduct Station was closed on 22nd January 1990. The line into Holborn Viaduct over Ludgate Hill was removed and a new line built that drops down steeply from Blackfriars station into a new station called City Thameslink (opened 29.5.1990) beneath the former Holborn Viaduct Station. The station was originally called St. Paul’s Thameslink but was renamed in 1991 to avoid confusion from St. Paul’s station on the Central line.
The northern part of the Thameslink network replaced the ‘Bedpan’ service from Bedford to St. Pancras and uses the existing Midland Main Line. In the south there are two branches. The main route runs through London Bridge to East Croydon and Brighton while the second branch initially ran into Guildford via West Croydon but has now been rerouted through Mitcham to terminate at Sutton.
Thameslink has become a significant commuter route serving the airports at Gatwick and Luton and carries around 40 million passenger journeys on the system annually.
Sources:
- A regional history of the railways of Great Britain - Volume 3 Greater London by H P White. David & Charles 1963 & 1971 ISBN 0 7153 5337 3
- London Railway Record Volume 18 January 1999 - Connor & Butler